Dosing and Administration
Prior to administering FOLOTYN, supplement patients with:
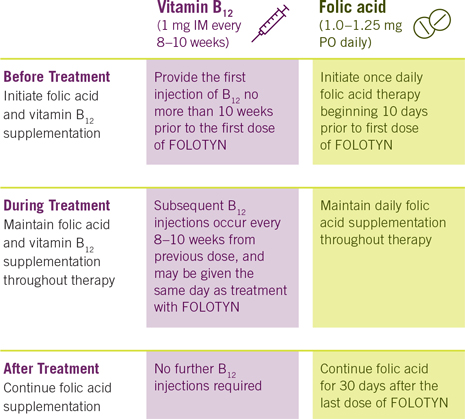
Important Monitoring Information
- Monitor complete blood cell counts weekly. Serum chemistry tests, including renal and hepatic function, should be performed prior to the start of the first and fourth dose of a given cycle
- Dose modifications are based on absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and platelet count prior to each dose
- Persistent liver function test abnormalities may be indicators of liver toxicity
and require dose modification or discontinuation - Monitor patients for renal function and systemic toxicity and adjust dosing accordingly
3-5 minute IV push administration.
7-week cycle.
The recommended dosage of FOLOTYN is 30 mg/m2 administered as an intravenous push over 3–5 minutes once weekly for 6 weeks, followed by 1 week of rest in a 7-week cycle1
- FOLOTYN is administered as an intravenous push over 3-5 minutes via the side port of a free-flowing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, intravenous line
- For patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15 to <30 mL/min/1.73m2), the recommended dose of FOLOTYN is 15 mg/m2. For patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, dose reduction is not necessary
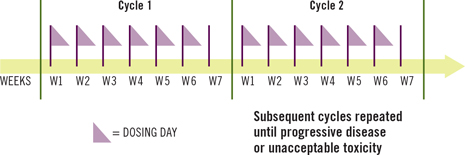
Important Dosing Information
- No pre-medications are required when administering FOLOTYN
- The calculated dose of FOLOTYN should be aseptically withdrawn into a syringe for immediate use. Do not dilute FOLOTYN
- Management of severe or intolerable adverse reactions may require dose omission, reduction or discontinuation of FOLOTYN therapy
Selected Safety Information
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Patients with moderate to severe renal function impairment may be at greater risk for increased exposure and toxicity. Monitor patients for renal function and systemic toxicity and adjust dosing accordingly. Avoid FOLOTYN use in patients with end stage renal disease including those undergoing dialysis unless the potential benefit justifies the potential risk.

FOLOTYN Drug Interactions
No formal clinical assessments of pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions between FOLOTYN and other drugs have been conducted1
The effect of co-administration of the uricosuric drug probenecid (an inhibitor of multiple transporter systems including the multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) efflux transporter) on pralatrexate pharmacokinetics was investigated in a Phase 1 clinical study. Co-administration of increasing doses of probenecid resulted in delayed clearance of pralatrexate and a commensurate increase in exposure.
When administering FOLOTYN to patients receiving probenecid or other drugs that may affect relevant transporter systems (eg, NSAIDs), monitor patients closely for signs of systemic toxicity due to increased drug exposure.
There are no contraindications for FOLOTYN.
- NDC 48818-001-01: 20 mg of pralatrexate in 1 mL solution in a vial (20 mg/1 mL)
- NDC 48818-001-02: 40 mg of pralatrexate in 2 mL solution in a vial (40 mg/2 mL)
Reference:
-
Folotyn [package insert]. East Windsor, NJ: Acrotech Biopharma, LLC.
FOLOTYN Important Safety Information
Indication
FOLOTYN® (pralatrexate injection) is a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
FOLOTYN Important Safety Information
Warnings and Precautions
- Myelosuppression: FOLOTYN can cause myelosuppression, manifested by thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and/or anemia. Monitor complete blood counts and omit and/or reduce the dose based on ANC and platelet count.
- Mucositis: FOLOTYN can cause mucositis. Monitor for mucositis weekly and omit and/or reduce the dose for ≥ grade 2 mucositis.
- Dermatologic Reactions: Dermatologic reactions, including fatal reactions, occurred and may be progressive and increase in severity with further treatment. Monitor closely and withhold or discontinue FOLOTYN based on severity.
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome: FOLOTYN can cause tumor lysis syndrome. Monitor patients who are at increased risk of TLS and treat promptly.
- Hepatic Toxicity: FOLOTYN can cause hepatic toxicity and liver function test abnormalities. Monitor liver function tests. Omit dose until recovery, adjust or discontinue therapy based on the severity.
- Risk of Increased Toxicity with Renal Impairment: Patients with severe renal function impairment may be at greater risk for increased exposure and adverse reactions. Reduce FOLOTYN dosage in patients with severe renal impairment. Avoid FOLOTYN use in patients with end stage renal disease with or without dialysis. If the potential benefit of administration justifies the potential risk, monitor renal function and reduce the dose based on adverse reactions.
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: FOLOTYN can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FOLOTYN and for 6 months after last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FOLOTN and for three months after last dose.
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions occurring in greater than 35% of patients were mucositis (70%), thrombocytopenia (41%), nausea (40%), and fatigue (36%). The most common serious adverse reactions occurring in more than 3% of patients were pyrexia, mucositis, sepsis, febrile neutropenia, dehydration, dyspnea, and thrombocytopenia.
Drug Interactions
- Avoid coadministration with probenecid or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). If coadministration is unavoidable, monitor for increased risk of adverse reactions.
Use in Specific Populations
- Lactation: Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with FOLOTYN and for 1 week after the last dose.
- Pregnancy Testing: Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiation of FOLOTYN
- Pediatric Use: The Safety and effectiveness of FOLOTYN in pediatric patients have not been established.
- Renal Impairment: Reduce the dose of FOLOTYN for patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15 to 29 mL/min/1.73 m2). No dosage modification is recommended for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment.
Please click here to see full Prescribing Information for FOLOTYN.
ISI-FOL-0180


